|
Full 54 Minute Video on Patreon:
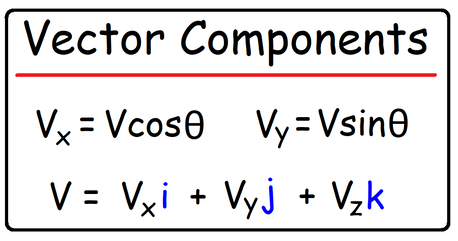
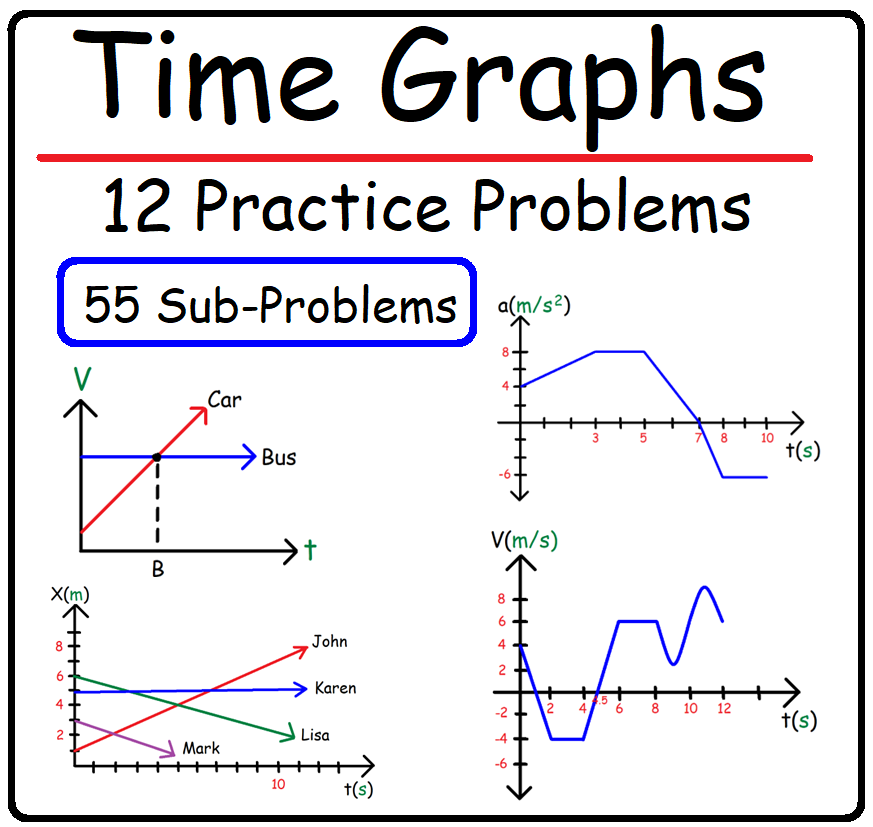
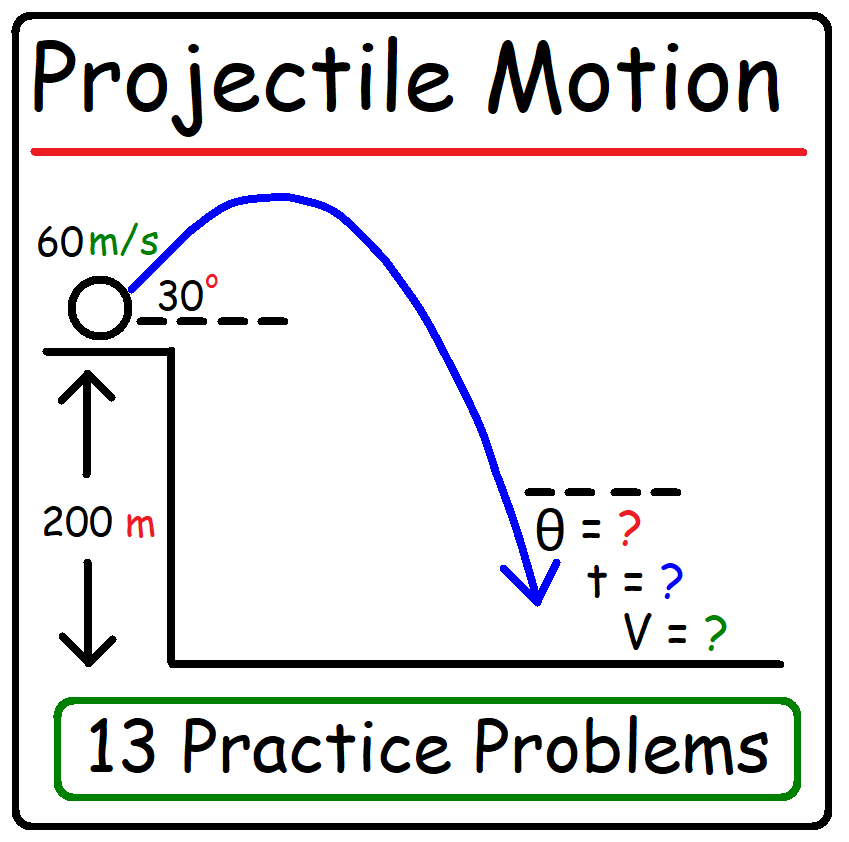
https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor Direct Link to The Full Video: https://bit.ly/3X4507F PDF Worksheet - 9 Questions: https://bit.ly/3vE2xVW Vectors - Basic Introduction A vector is quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, and Momentum are vectors because they can be describe not only in terms of magnitude (big or small) but also in terms of direction (east or west). Mass, Temperature, Distance, and Speed are scalar quantities because direction is irrelevant. Vector Components: A 2D vector can be decomposed into its x and y components. For instance, the velocity vector V has a horizontal component Vx and a vertical component Vy. A 3D velocity vector has three components - Vx, Vy, and Vz. For a 2D vector, the horizontal velocity component Vx is the product of the magnitude of the velocity vector and the cosine of the counter clock-wise angle that the vector makes with the +x-axis. Similarly, the vertical velocity component Vy is equivalent to Vsin(angle). The components of a vector can be expressed in terms of the unit vectors i, j, and k. A force vector with the value F = 50i - 90j tells you that the horizontal component Fx = +50 and the vertical component Fy = -90. A velocity vector with the value V = 5i - 3j + 7k tells you that Vx = 5, Vy = -3, and Vz = 7. Free Fall Physics Problems: www.video-tutor.net/free-fall-equations.html Motion Time Graphs - Velocity Time Graphs: www.video-tutor.net/motion-time-graphs.html How To Find The Resultant of Two Vectors: www.video-tutor.net/resultant-two-vectors.html Video Playlists and Final Exam Videos: www.video-tutor.net/ |